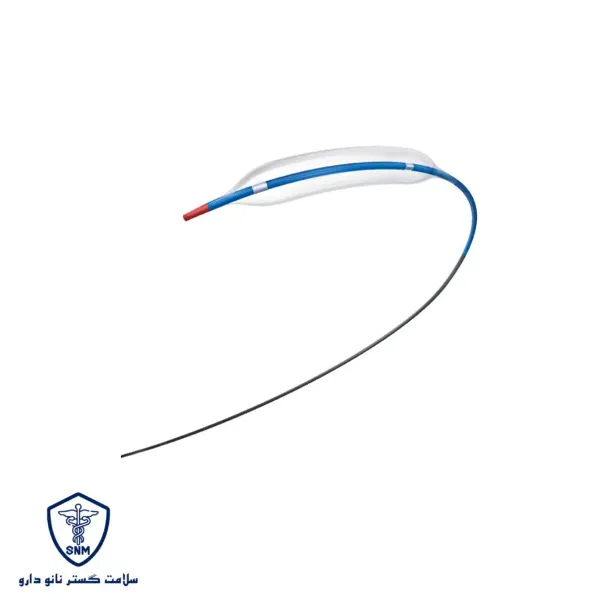
During the balloon angioplasty procedure, a balloon catheter is guided through an artery (often the femoral artery in the thigh) to the blocked blood vessels. Once the balloon reaches the narrowed or blocked area, it is gently inflated, applying pressure to the vessel walls, widening the artery, and improving blood flow. After the vessel is opened, the balloon is deflated, and the catheter is removed. In some cases, a stent (a metallic mesh) is inserted alongside the balloon to ensure the vessel remains open long-term.
Endovascular balloons come in various types based on material, size, and design features:
Conventional Balloons: These are standard balloons used to open vascular blockages.
Drug-Coated Balloons: These balloons are coated with anti-proliferative drugs that are delivered to the vessel walls upon inflation, preventing the reformation of plaques.
Cutting Balloons: Equipped with small ridges or blades, these balloons help remove tougher plaques and open advanced blockages.
Endovascular Balloon Sizes
Endovascular balloons are available in different diameters and lengths. Their diameter typically ranges from 1.5 to 10 millimeters, and their length can vary from a few millimeters to 10 centimeters. Selecting the appropriate balloon size depends on the vessel’s size and location, the severity of the blockage, and the surgical requirements.
Advantages of Endovascular Balloons
Endovascular ballooning is a minimally invasive and effective method for treating vascular stenosis, helping patients resolve vessel blockages without open surgery. This technique significantly improves blood flow and reduces the likelihood of disease recurrence. However, proper usage requires precision and should be performed by skilled surgeons, with careful selection of the balloon type and size being crucial.
With its variety of types and sizes, the endovascular balloon is a powerful tool for reopening blocked vessels and enhancing blood flow throughout the body. This minimally invasive method reduces the need for open surgeries and contributes to improving patients’ quality of life. Its application demands careful consideration of patient conditions and the nature of the vascular blockage.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.