The inflator is one of the key tools used in angioplasty and other cardiovascular interventional procedures to precisely control the pressure inside angioplasty balloons. It allows doctors to inflate specific balloons within blood vessels safely and accurately, adjusting the pressure applied.
In angioplasty, when a coronary artery becomes blocked or narrowed, a small balloon is used to open the blood flow pathway. The inflator’s role in this process is to regulate the pressure and control the inflation and deflation of the balloon, ensuring the vessels are widened without damaging their walls.
This device is not only used in coronary angioplasty for treating heart vessel diseases but also in peripheral vascular interventions to clear blockages in other body vessels. Additionally, during stent placement, the inflator ensures the stent is positioned correctly and securely adheres to the artery wall.
Given the critical need for precision in cardiovascular interventions, choosing a high-quality and accurate inflator plays a vital role in enhancing patient safety and the success of the procedure.
Applications of the Inflator in Medicine
In addition to coronary angioplasty, the inflator is used in various other medical treatments related to cardiovascular diseases, peripheral vessels, and even some modern therapies. Due to its ability to control pressure safely and accurately, this device is employed in various medical scenarios. Below are some of the most important applications of the inflator:
Coronary Angioplasty (Treatment of Heart Diseases)
One of the primary and most common uses of the inflator is in coronary angioplasty. This procedure is performed for patients suffering from conditions like atherosclerosis or coronary artery blockage, leading to reduced blood flow, chest pain (angina), or heart attack.
In angioplasty, the doctor uses a balloon catheter connected to the inflator. The catheter is inserted through the femoral artery (in the groin) or radial artery (in the wrist) and guided to the blockage site. Then, by inflating the balloon with the inflator, fatty plaques causing the artery narrowing are compressed, and the vessel is opened.
Benefits of Using an Inflator in Coronary Angioplasty:
Precise Balloon Pressure Control: The inflator adjusts the pressure so that the balloon inflates sufficiently without damaging the vessel walls, ensuring the artery opens.
Helps Prevent Re-blockage: After balloon inflation, a stent is often used to keep the artery open. The inflator plays a crucial role in placing the stent accurately.
Enhances Procedure Safety and Accuracy: Improper pressure settings can lead to vessel damage or failure to clear the blockage. The inflator helps maintain precise pressure adjustments.
Peripheral Vascular Interventions (Treatment of Blockages in Limbs and Other Vessels)
The inflator is also used in treating peripheral vascular diseases (such as those affecting blood vessels in the arms, legs, and kidneys). In conditions like peripheral artery disease (PAD), fatty plaque buildup in the arteries of the legs reduces blood supply to the muscles, causing symptoms like pain, numbness, slow-healing wounds, and even gangrene (tissue death).
In such cases, the doctor uses the inflator to inflate the balloon to open the narrowed peripheral vessels and may place a stent if necessary to keep the vessel open.
Why is the Inflator Important in Peripheral Vascular Treatment?
Precise pressure control helps open narrowed vessels, improving blood flow.
Enhances the patient’s quality of life by reducing symptoms of blockages and improving mobility.
Prevents the need for complex surgeries like bypass surgeries for peripheral vessels.
Treatment of Vascular Stenosis Due to Chronic Diseases (Diabetes, Hypertension, and Kidney Disease)
Diseases like diabetes, high blood pressure, and kidney failure can cause narrowing of blood vessels and reduced blood flow to various parts of the body. These issues can affect the kidneys, brain, legs, and even the eyes (diabetic retinopathy).
One treatment approach for these patients is peripheral and renal angioplasty using the inflator. In this procedure, the doctor uses a balloon catheter and inflator to open blockages and restore blood flow to vital organs.
Why is this Method Important for Diabetic and Hypertensive Patients?
Reduces the risk of amputation in diabetic patients with leg vessel blockages.
Improves kidney function in patients with kidney issues due to hypertension or diabetes.
Lowers the risk of stroke in patients with brain vessel blockages.
Use of the Inflator in Modern Medical Treatments and Research
With advancements in therapeutic technologies, the inflator is also utilized in innovative and research-driven procedures. Some new applications of this device include:
Drug-Coated Angioplasty: In this method, the balloon is coated with anti-blockage drugs (like paclitaxel) and releases the drug as it inflates. The inflator helps ensure the drug is transferred evenly to the artery walls, reducing the risk of re-blockage.
Aneurysm Treatment: An aneurysm is an abnormal enlargement of a blood vessel that can rupture. In some cases, inflators are used in aneurysm closure procedures or placing specific stents inside them.
Regenerative Medicine Research: Some studies have shown that using the inflator in stem cell implantation procedures on damaged blood vessel walls can help repair damaged tissues.
Inflator Introduction
Important Features of a Quality Inflator
Choosing the right inflator directly affects the accuracy, safety, and success of angioplasty and vascular interventions. Doctors need to precisely adjust the pressure, clearly view information, and ensure smooth and reliable performance during use. Below are some key features of a high-quality inflator:
High-Precision Pressure Adjustment A top-quality inflator must allow for precise pressure control. The balloon pressure used to open blood vessels needs to be controlled to:
- Prevent over-expansion or insufficient inflation.
- Allow for fine, controlled adjustments, especially in sensitive interventions where small pressure changes can significantly impact the outcome.
- Maintain stable pressure over time, without losing accuracy due to environmental changes or prolonged use. A high-quality inflator usually features advanced control systems that display real-time pressure, allowing for immediate adjustments.
Ergonomic and User-Friendly Design Since doctors may work with the inflator for extended periods, the device’s design should be comfortable, lightweight, and user-friendly to ensure easy control. Key ergonomic design aspects include:
- Comfortable, non-slip handle: ensuring full control during use.
- Balanced, lightweight construction: making prolonged use easier.
- Quick and simple operation: controls should allow for pressure adjustments with minimal effort.
- One-handed operation: allowing the doctor to adjust pressure with minimal movement and high precision when needed.
Clear and Accurate Display During the procedure, the doctor needs to quickly and clearly see the pressure and volume data. Therefore, a clear and accurate display is a must-have feature in an inflator.
- Numbers should be large and easy to read for immediate visibility.
- Backlighting can enhance readability in low-light or specific conditions.
- Some advanced inflators include a warning system that notifies the doctor when the pressure exceeds the safe range.
Appropriate Volume and High Injection Accuracy A high-quality inflator should have sufficient capacity to inject fluid into the balloon. If the volume is insufficient, the doctor may need to adjust multiple times, disrupting the treatment process.
- Minimal pressure fluctuation: ensuring gradual, precise injection without sudden pressure changes.
- Accurate control of injected volume: some models offer adjustable settings to finely tune the volume.
- Maintaining injected volume for a long duration without leakage or pressure loss.
High Build Quality and Durability Since inflators are sensitive medical instruments, they must be made from high-quality materials to ensure that their performance and accuracy remain consistent over time.
Constructed from wear- and corrosion-resistant materials such as medical-grade polymers and stainless steel.
- Resistant to leaks and pressure drops to prevent sudden performance changes.
- Capable of maintaining accuracy long-term without requiring frequent recalibration.
- Can be sterilized and resistant to medical disinfectants without compromising quality.
Versatility for Different Conditions and Treatment Methods Advanced inflators typically come with features that make them suitable for a variety of medical treatments.
- Compatibility with different types of balloons: the inflator should work with a wide range of medical balloons, making it suitable for coronary angioplasty, peripheral procedures, aneurysm treatment, and more.
- Environmental resistance: it should perform reliably in varying temperatures and conditions.
- Integration with hospital systems: some modern inflators can connect to monitoring systems, enabling digital recording of pressure and volume data for better tracking and analysis.
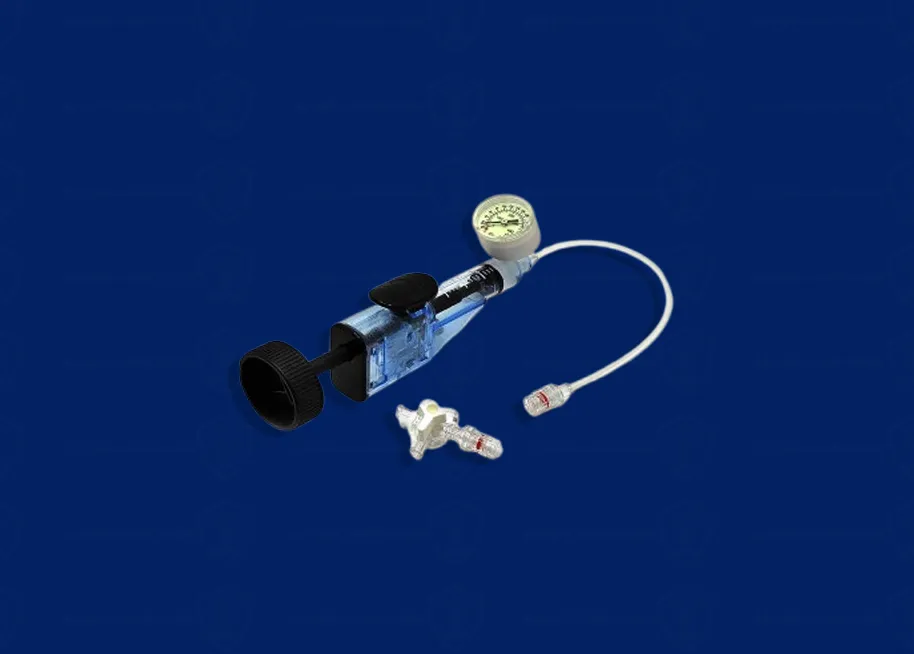

Inflator Introduction
If you’d like, you can view this product on our website and get more information. Also, if you have any questions or need assistance, the support team of Salamat Gostar Nano Daroo is available during working hours. For quicker communication, feel free to contact us via WhatsApp.

