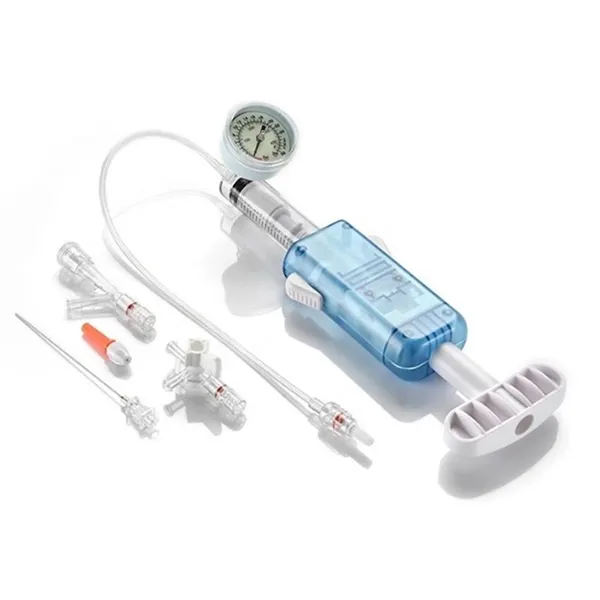
The inflator typically consists of the following components:
Manometer (Pressure Gauge): Provides accurate pressure readings for the physician.
Piston and Syringe: Ensures precise fluid injection or withdrawal into the balloon.
Safety Valve: Allows for rapid and safe fluid release from the balloon in emergencies.
Adjustable Handle: Facilitates more precise control during fluid injection.
Inflators are usually made of durable materials such as plastic or lightweight metals and are ergonomically designed to ensure ease of use for healthcare professionals.
Sizes and Capacities
Inflators come in various sizes and capacities, tailored to meet different medical needs. Their variations are often defined by:
Fluid Volume Capacity: Typically ranging from 20 to 30 cc.
Pressure Range: Adjustable pressures, often up to 20 or 30 atmospheres.
Types of Inflators
Manual Inflator:
Operates through a piston and manual pressure applied by the physician. Due to its simplicity, it is widely used in many medical procedures.
Digital Inflator:
A more advanced model featuring a digital display, allowing the physician to monitor and control pressure and volume with greater precision. This type is particularly useful in complex cardiac interventions requiring meticulous control.
Applications
Inflators are commonly employed in:
Coronary angioplasty procedures.
Treatment of aneurysms.
Other vascular procedures and arterial blockage treatments.
Inflators are essential tools for controlling pressure in medical balloons, enabling physicians to treat vascular blockages with greater precision. With their diverse types and advanced features, inflators have become indispensable in cardiology and other critical surgical domains.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.